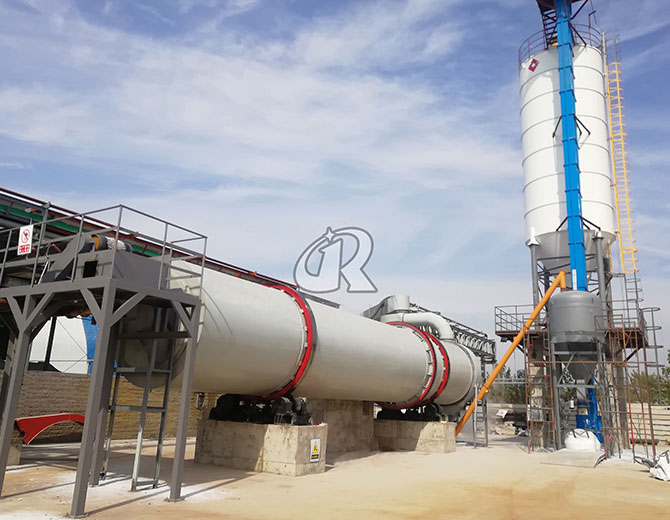
Rotary Dryers have many applications but are most commonly seen in the mineral industry for drying sand, stone, soil, and ore. In addition, it is also often used to dry biomass, wood chips, palm shell, coconut shell, animal manure, sludge, coal slime, etc.
The material enters the inner layer of the rotary drum from the feeding device to realize downstream drying. The material is continuously picked up and scattered under the copying plate of the inner layer in a spiral manner to realize heat exchange, and the material moves to the other end of the inner layer and enters the middle layer. For countercurrent drying, the material is continuously and repeatedly raised in the middle layer, in a way of advancing two steps and one step back. The material in the middle layer not only fully absorbs the heat emitted by the inner drum, but also absorbs the heat of the middle drum, and at the same time prolongs the drying time. time, where the material reaches the desired dry state. The material travels to the other end of the middle layer and falls into the outer layer. The material travels in a rectangular multi-loop way in the outer drum. The material that achieves the drying effect quickly travels and exits the drum under the action of hot air. The wet material that does not achieve the drying effect cannot be quickly due to its own weight. When traveling, the material is fully dried in this rectangular copy board, thereby completing the drying purpose.
| Product Standard(m) | Capacity(t/h) | Feed moisture(%) | Final Moisture(%) | Power(KW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.8*8 | 0.5-3 | 30% | 15%-1% | 3KW |
| 1*10 | 1-5 | 30% | 15%-1% | 5.5KW |
| 1.2*12 | 2-8 | 30% | 15%-1% | 11KW |
| 1.6*16 | 6-10 | 30% | 15%-1% | 15KW |
| 1.8*16 | 8-15 | 30% | 15%-1% | 18.5KW |
| 2*18 | 10-20 | 30% | 15%-1% | 22KW |
| 2.2*18 | 12-25 | 30% | 15%-1% | 30KW |
| 2.4*22 | 15-30 | 30% | 15%-1% | 45KW |
| 2.6*24 | 18-35 | 30% | 15%-1% | 55KW |

